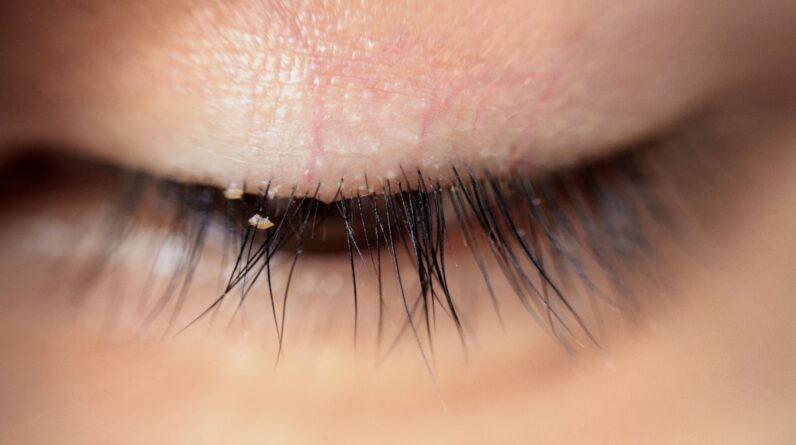
Tarsus Pharmaceuticals Inc. announced today that the FDA has approved lotilaner 0.25% ophthalmic solution for the treatment of Demodex blepharitis. (Image courtesy of Adobe Stock)
Tarsus Pharmaceuticals Inc. announced that the FDA approved lotilaner 0.25% ophthalmic solution (XDEMVY) for the treatment of Demodex blepharitis. Lotilaner 0.25% Ophthalmic Solution, formerly known as TP-03, is the first and only FDA-approved treatment to directly target Demodex mites, the primary cause of Demodex blepharitis.
“We are pleased to announce the FDA approval of XDEMVY for the treatment of Demodex blepharitis and look forward to making this product widely available to the millions of patients who have not had an FDA-approved therapeutic for this condition,” said Bobak Azamian, MD, PhD, CEO and President of Tarsus, in a press release. “This tremendous milestone was achieved through a successful collaboration between our talented team at Tarsus, countless eye care providers, and the hundreds of patients who participated in our trials. We are grateful and honored for the opportunity to introduce the first and only approved therapeutic for this disease to the eye care community.”
According to the company’s press release, the FDA approval is based on the results of two randomized, multicenter, double-masked, vehicle-controlled studies (Saturn-1 and Saturn-2), designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of XDEMVY in 833 patients, 415 of whom received lotilaner ophthalmic solution. Patients with Demodex blepharitis were randomized to lotilaner ophthalmic solution or vehicle in a 1:1 ratio and dosed twice daily in each eye for 6 weeks.
The company noted that efficacy was demonstrated by significant eyelid improvement (reduction of collars, the pathognomonic sign of the disease, to no more than 2 collars per upper eyelid) in each study by day 43, with some patients seeing improvement as early as 2 weeks. In addition, the endpoints of mite eradication (mite density of 0 mites per lash) and cure of erythema (Grade 0) showed statistically significant improvement at day 43 in both studies. In clinical trials, XDEMVY was generally safe and well tolerated. The most common ocular adverse reactions observed in the studies were itching and burning at the instillation site, which was reported in 10% of patients. Other ocular adverse reactions reported in less than 2% of patients were chalazion/hordeolum (barley) and punctate keratitis.
Christopher Starr, MD, associate professor of ophthalmology, director of Refractive Surgery, Ophthalmic Education and the Cornea Fellowship Program at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York Presbyterian Hospital, noted in the press release that after years of seeing Demodex blepharitis in his practice without an effective way to target the root cause of the disease, he is now happy to offer a new treatment to his patients.
“Easily diagnosed by the presence of eyelash collars, Demodex blepharitis can cause eye damage in multiple ways, including irritation, loosening or loss of eyelashes, and inflammation, which can be uncomfortable for patients,” he said in the press release. “This new drug is a positive step forward for the treatment of this disease in many patients who have been fighting it for years.”
Demodex blepharitis affects approximately 25 million eye care patients in the US, or 1 in 12 adults. It is a common but often misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed eyelid disease caused by an infestation of Demodex mites, the most common ectoparasite found on human skin. Demodex blepharitis is characterized by redness, inflammation, missing or misdirected eyelashes, horizontal itching along the base of the eyelid, and the presence of collars. Collarettes are cylindrical, waxy remnants of mite debris and eggs found at the base of the eyelashes.
“More than half of the patients in my practice have Demodex blepharitis, and until now we have had no FDA-approved therapy to treat the condition,” Selina McGee, OD, FAAO, BeSpoke Vision, said in the press release. “Many patients have experienced redness, crusting and general eye discomfort for years, and I’m excited to finally be able to offer an FDA-approved treatment to my patients.”
For more information about lotilaner ophthalmic solution and complete prescribing information, visit www.xdemvy.com.
[ad_2]
Source link





